Colorectal cancer – Everything you need you
- 2241 Views
- Apollo Hospital Mumbai
- September 15, 2020
- Oncology
Colorectal cancer – Everything you need you
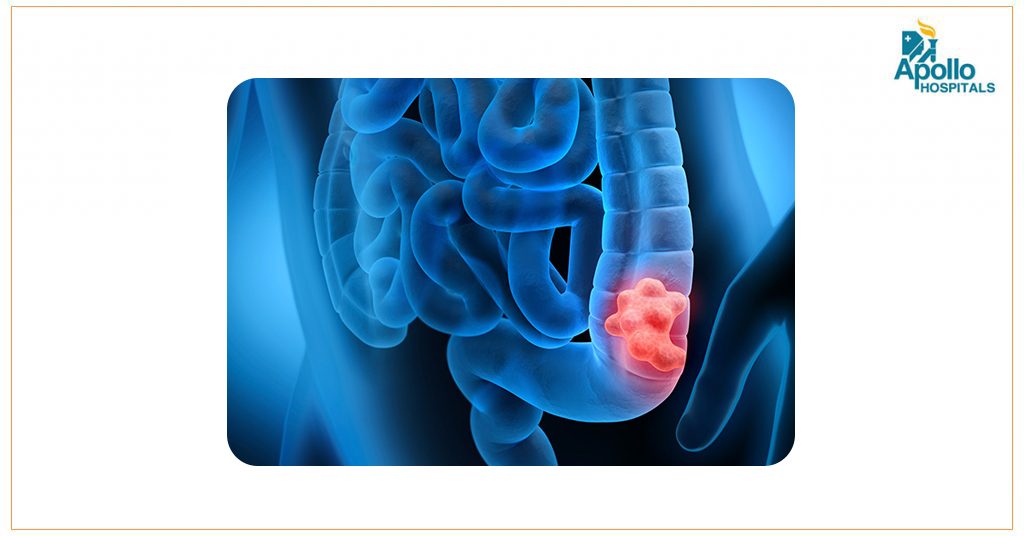
Colorectal cancer is one of the slowest growing cancers. The major challenge,however, lies in its detectionas its major symptoms aren’t visible in the initial stages. Colorectal cancer can be completely cured, if detected early.
The colon and rectum are parts of the digestive system. Food matter is largely broken down in the stomach and then released into the small intestine, where most of the nutrients are absorbed. The small intestine continues into the colon, which is divided into 4 regions (based on location): ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, and sigmoid colon. The function of the colon is to absorb water and mineral nutrients from the food matter and store waste. Waste moves from the colon into the final 6 inches of the digestive system, called the rectum, and passes out of the body through the anus. About 95% of colorectal cancers develop in the cells lining the colon and rectum.
A cancer that begins in a glandular cell is called an adenocarcinoma. Cancer usually starts in the innermost layer of the lining and slowly progresses through the other layers.
Risk Factors:
- Family history
- People with chronic inflammatory bowel diseases
- People over the age of 50
- Obesity
- Physically inactive
- People who eat less fibre and more of red, processed meat
- Smoking
- Excessive alcohol consumption
Symptoms visible in the advanced stages of colorectal cancer:
- Bleeding in the rectum
- Stools with blood (Can be bright red or dark depending on the location of the tumour)
- A change in bowel habits
- Cramps in the colorectal region
- Anaemia from the blood loss
- Weakness and fatigue
- Decreased appetite or weight loss
Screening Tests (Above 50 years):
- Sigmoidoscopy, recommended every 5 years
- Colonoscopy, recommended every 10 years
- Double contrast barium enema every 5 years,
- CT Colonography (virtual colonoscopy) every 5 years
- Digital rectal examination
- Faecal occult blood test (FOBT) every year
- Faecal immunochemical test (FIT) every year
- Stool DNA test (sDNA test)
- In people with family history of colon cancer screening should start at 40 years of age
Treatment:
Treatment of colorectal cancer is decided post staging analysis of the disease. The stages of a colorectal cancer are determined by the depth of invasion through the wall of the intestine; the involvement of the lymph nodes (the drainage nodules); and the spread to other organs (metastases).
Early Stage: For cancers that are stage 0—also known as carcinoma in situ—the disease remains within the lining of the colon or rectum. Therefore, removal of the cancer, either by polypectomy via colonoscopy or by surgery (if the lesion is large) is thecommon course of treatment.
Stage 1: Stage 1 colorectal cancers grow into the wall of the intestine but have not spread beyond its muscular coat. The standard treatment of a stage I colon cancer is usually surgery alone, in which the affected part of the colon and its lymph nodes are removed.
Stage 2: Stage 2 colorectal cancer penetrates beyond the muscular layers of the large intestine (stage 2B) and even spreads into adjacent tissue (stage 2C). Usually the only treatment for this stage of colon cancer is a surgical resection, although chemotherapy after surgery may be added. For a stage 2 rectal cancer, a surgical resection is sometimes preceded or followed by chemotherapy and/or radiation.
Stage 3: Stage 3 colorectal cancer is considered an advanced stage of cancer as the disease has spread to the lymph nodes. Chemotherapy and radiation may precede or follow surgery for this stage.
Stage 4: In stage 4 colorectal cancer, the disease spreads (metastasized) to distant organs such as the liver, lungs, or ovaries. Occasionally the cancer’s spread is restricted enough to where it can all be removed by surgery. In the case of minimal disease in the liver, the tumour may be treated with radiofrequency ablation (destruction with heat), cryotherapy (destruction by freezing), or intra-arterial chemotherapy. For stage 4 cancer that cannot be surgically removed, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or both may be used to relieve, delay, or prevent symptoms.
- January 20, 2025
Total Knee Replacement: The Role of Robotics
- January 20, 2025
Awareness and Precautions Against Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)
- January 20, 2025
Aortic Root Replacement
- December 26, 2024
Robotic Surgery in Orthopedics
- Bone Marrow Transplant3
- Cardiac sciences44
- Cardiology1
- Child Care7
- Clinical Excellence33
- Cosmetology2
- COVID-199
- Diseases4
- Emergency10
- Emergency8
- Endocrinology1
- ENT5
- Fetal Medicine1
- Gastroenterology8
- General Medicine11
- General Surgery4
- Genomic Medicine2
- Gynecology1
- Health14
- Hematology2
- Kidney Transplant5
- Kidney Transplant2
- Liver Transplant6
- Neonatology1
- Nephrology2
- Nephrology & transplant1
- Nephrology & Urology4
- Neurosciences21
- Neurosciences1
- Nutrition/Diet1
- Obstetrics & Gynecology9
- Obstetrics & Gynecology4
- Oncology3
- Oncology93
- Ophthalmology1
- Orthopedic15
- Patient Speak1
- Pediatric Surgery4
- physiotherapy2
- Psychologist2
- Pulmonology4
- Rheumatology1
- Robotic Suregry1
- Robotic Surgery11
- Spine1
- Uncategorized111
- Urology1
- Women Care5
