Could not find the what you are looking for?
Alcoholic and non-alcoholic liver disease
Published On February 18, 2025
Verified by: Dr. Purshottam Vashisht- Consultant Gastroenterology, Apollo Hospitals Navi Mumbai
Dr. Deven Gosavi- Associate Consultant Gastroenterology, Apollo Hospitals Navi Mumbai
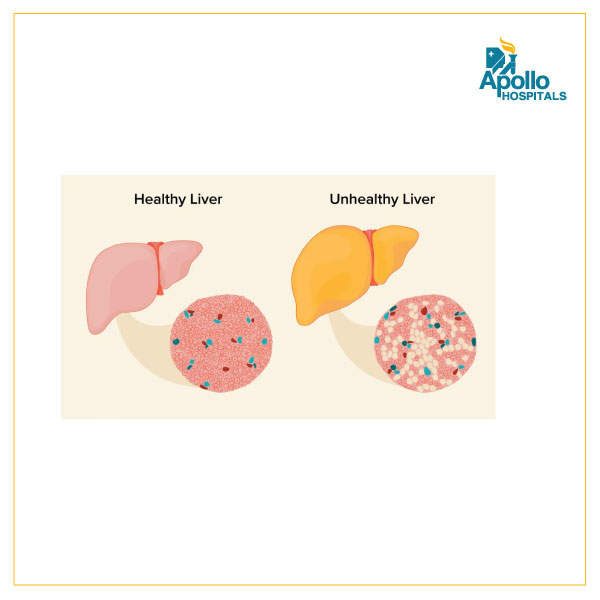
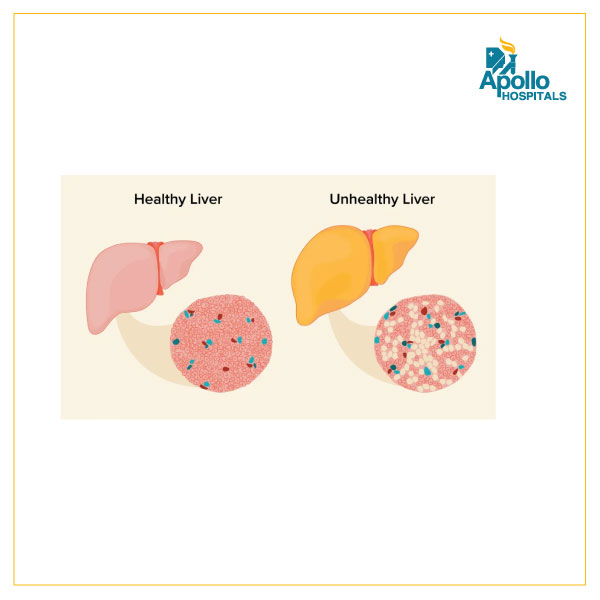
The liver is a vital organ responsible for a variety of functions in the body, including the metabolism of alcohol. Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to damage to the liver, leading to Alcoholic Liver Disease (ALD). However, liver disease can also occur in people who do not consume alcohol, known as Non-alcoholic Liver Disease (NALD).
Alcoholic liver disease (ALD) is a broad term that encompasses a spectrum of liver diseases caused by excessive alcohol consumption. The three main types of ALDs are Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD), alcoholic hepatitis, and alcoholic cirrhosis. AFLD is the earliest stage of ALD and is characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver. Alcoholic hepatitis is a more severe form of ALD that can lead to liver failure and cirrhosis. Alcoholic cirrhosis is the most advanced stage of ALD and can lead to liver failure and death. Risk factors for ALD include excessive alcohol consumption, gender (men are more likely to develop ALD than women), genetics, and malnutrition.
Non-alcoholic liver disease (NALD) is a group of conditions that affect the liver but are not caused by alcohol consumption. The two main types of NALD are Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH). NAFLD is the most common type of NALD and is characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver. NASH is a more severe form of NAFLD that can lead to liver scarring, liver failure and liver cancer. The risk factors for NALD include obesity, type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol, and high blood pressure.
Symptoms
The symptoms of both ALD and NALD can be similar and may include fatigue, weakness, weight loss, abdominal pain, and jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes). However, in some cases, there may be no symptoms at all.
Treatment & Prevention
Treatment for both ALD and NALD involves making lifestyle changes, such as reducing alcohol consumption or losing weight, and may involve medication. In severe cases, liver transplantation may be necessary.
Prevention of both ALD and NALD involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, such as limiting alcohol consumption, eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy weight. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can also help detect liver disease early.
In conclusion, both alcoholic and non-alcoholic liver diseases can lead to serious liver damage and require early detection and intervention. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and seeking medical attention when symptoms arise are essential in preventing and treating both ALD and NALD.



