What is Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Haemorrhage?
What is subarachnoid haemorrhage?
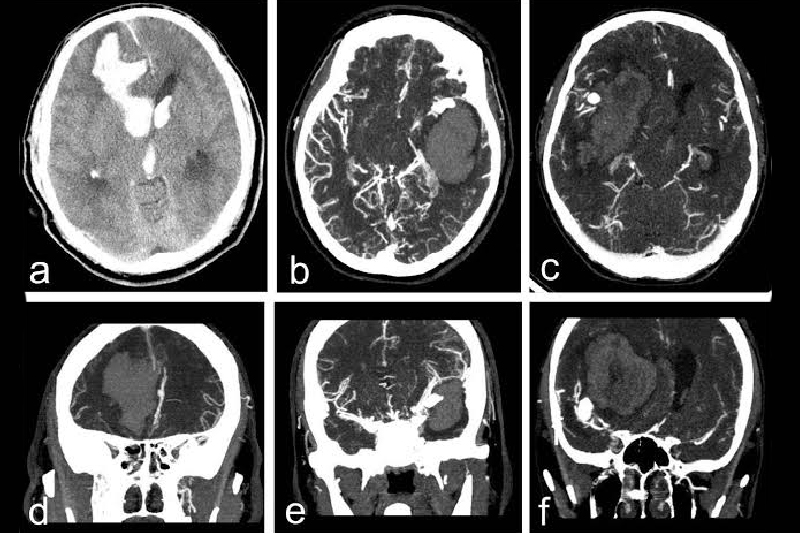
Subarachnoid haemorrhage is intracranial bleeding, due to rupture of a vessel or a bleb in the vessel, in the CSF spaces around the brain generally at the basal cisterns.
How does a patient with subarachnoid haemorrhage present?
A patient with subarachnoid haemorrhage presents with sudden severe headache. Varying degrees of impairment of consciousness and neurological deficits such as hemiparesis or speech deficit may be present.
What is the cause of subarachnoid haemorrhage?
Intracranial vessel aneurysm is the commonest cause. Head injury and arterio-venous malformations are some of the other causes.
What is an intracranial aneurysm?
Aneurysm is an outpouching or bleb of the involved arterial vessel wall and forms due to a focal weakness of the wall.
It is commonly found in the vessels of circle of Willis at the base of the brain.
Small aneurysms may remain undetected till investigated for, after a bleeding episode.Large ones may present with mass effect.
Atherosclerosis, hypertension, drug abuse and alcohol abuse are some of the risk factors associated.
A small percentage of the patients have associated conditions like polycystic kidney disease, coarctation of aorta, aortic valve stenosis, Marfan syndrome, Ehlers Danlos syndrome etc.
Risks and prognosis in subarachnoid haemorrhage due to aneurysmal rupture.
Aneurysm rupture is associated with high morbidity in the form of neurological deficits and also high mortality.
If not treated Re-bleeding rates are high and almost 50% re-bleed in the first six months.
How is subarachnoid haemorrhage due to aneurysmal rupture managed?
Aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage requires immediate hospitalization and intensive care management.
Medical imaging in the form of CT/MRI will be required to define the extent of haemorrhage and source of bleeding.
Medical treatment for recovery from intracranial bleeding will be started in intensive care unit.
Early treatment procedure to secure and protect the aneurysm from re-rupture will be required.
What treatment procedure options are available to protect the aneurysm from re-rupture?
- A) Neurosurgery involves open surgery to expose and clip the aneurysm.
- B) Neurointerventional treatment is the image guided less invasive endovascular procedure.
About Neurointerventional endovascular treatment of aneurysm (Also known as coiling procedure)
Neurointerventional endovascular treatment of aneurysm does not involve open surgical approach. It is performed endovascularly, i.e. from inside the vessel, after gaining access through a groin arterial route.
Hence it is less invasive with less damage to the surrounding brain and consequentlyless resultant complications.
The recovery time is shorter and clinical outcome is better as borne out in ISAT trial and other studies.
Neurointerventional endovascular procedure is considered as a first choice in these cases especially if the setup is available (Like in Apollomedics Super Speciality Hospitals Lucknow). In some cases the vascular anatomy may not be suitable. In these cases Neurosurgical treatment is offered.
How is it performed?
It is performed by a trainedNeurointerventional Radiologist in an advanced Digital subtraction angiography suite, preferably a bi-plane set up.
Under general anaesthesia, endovascular approach is obtained through the groin artery (femoral artery).
Under X ray fluoroscopy Roadmap guidance micro catheter tip (fine tube) is placed in the aneurysm through endovascular route.
Detachable platinum coils are placed inside the aneurysm to pack it under image guidance.
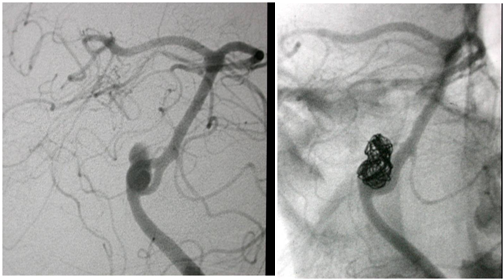
Fig 1 A & B: A basilar artery fenestration aneurysm before (A) and after (B) coiling.
The platinum coils are biologically inert and MRI compatible.
The aneurysm is occluded from inside leaving the parent vessel intact often with the help of a balloon catheter.
Adjuvant stent may be required in some cases.
Aneurysm thus coiled stays occluded and is evaluated with MR angiography at follow up.
What to expect after Neurointerventional endovascular treatment (Coiling procedure)?
After a coiling procedure the patient will be managed in an intensive care unit, usually for a couple of days and a standard neuro- intensive care for subarachnoid haemorrhage will be instituted.
This includes treatment for neurological deficits associated with subarachnoid haemorrhage and hydrocephalus/vasospasm if any, and peri-procedural complications if any.
Some patients my need additional treatment for vasospasm and some may require External Ventricular Drainage (EVD) or ventricular shunt.
Supportive physiotherapy is given while in the ward and after discharge if necessary.
Usually the patient will be discharged, once stable, with an advice for medications for a period of 6 weeks or longer.
Clinical follow up review is generally done at 6 weeks and that along with MR angiography at 6 months and 18 months.